Hypertension: Managing High Blood Pressure
Dr. Jane Doe
7 Sep 2024 • 8 min read
Introduction to Hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a common condition where the force of blood against the artery walls is consistently too high. This can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Managing hypertension effectively involves lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring.

What is Hypertension?
Hypertension is defined as having a blood pressure reading of 140/90 mm Hg or higher. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) and recorded with two numbers: systolic pressure (the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats) over diastolic pressure (the pressure in the arteries when the heart rests between beats).
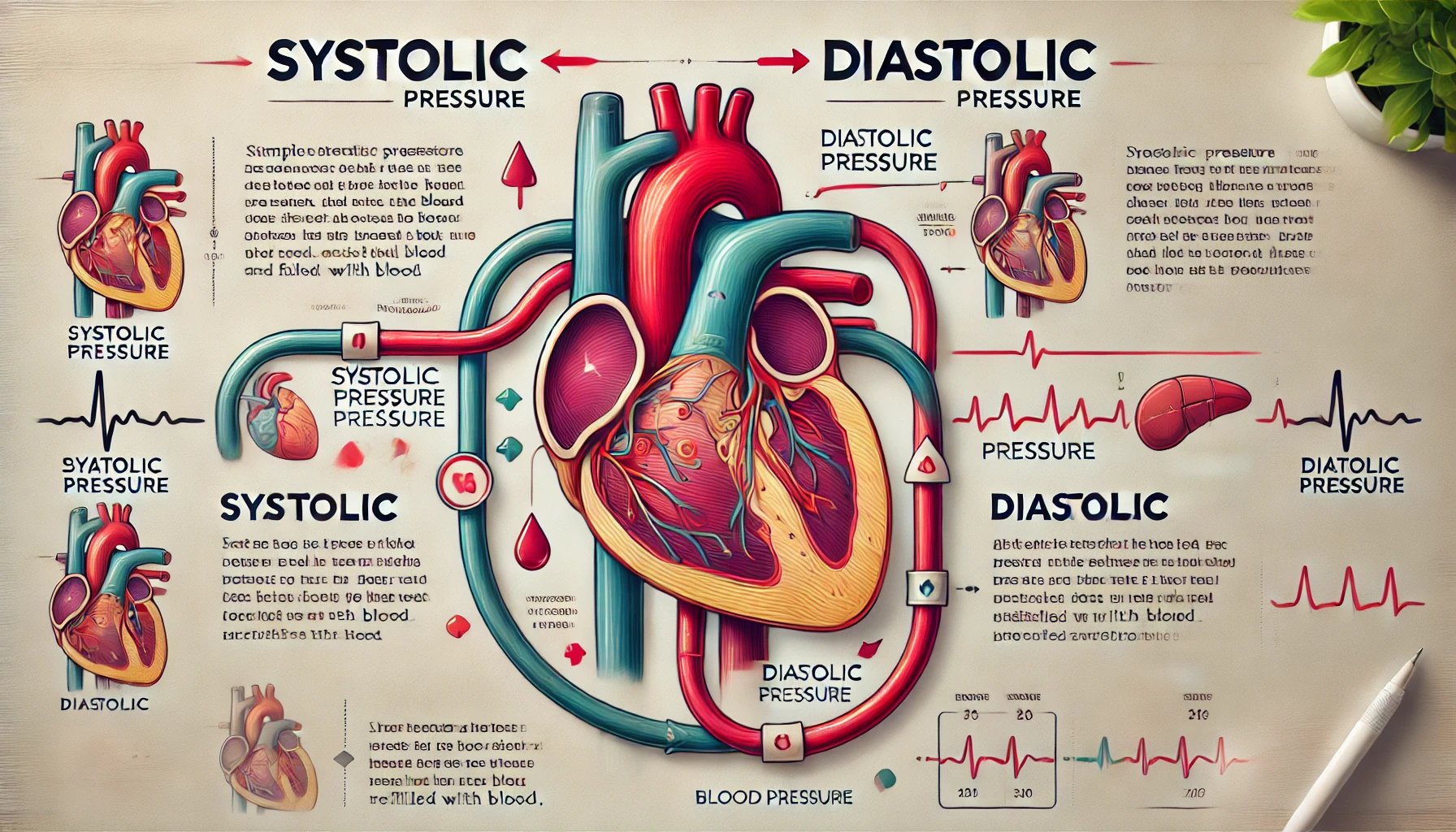
Types of Hypertension
- Primary (Essential) Hypertension: This type develops gradually over many years and has no identifiable cause.
- Secondary Hypertension: This type is caused by an underlying condition such as kidney disease, hormonal disorders, or the use of certain medications.
Symptoms of Hypertension
- Severe Headaches: Persistent headaches can be a symptom of high blood pressure.
- Fatigue or Confusion: Mental fog or confusion may be linked to hypertension.
- Vision Problems: Blurred or double vision may indicate high blood pressure.
- Chest Pain: Chest discomfort is a serious symptom that requires immediate attention.
- Difficulty Breathing: Shortness of breath can result from hypertension-related complications.
- Irregular Heartbeat: Palpitations or an irregular pulse may occur.
- Blood in Urine: High blood pressure can damage kidneys, causing blood to appear in the urine.
- Pounding Sensation: Feeling a pulse in the neck, ears, or chest.

Causes and Risk Factors
Hypertension can result from a variety of causes and risk factors, some of which are controllable.
- Genetic Factors: Family history plays a significant role in hypertension.
- Age: The risk increases with age.
- High Salt Intake: Excessive salt consumption raises blood pressure.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles contribute to hypertension.
- Obesity: Being overweight puts extra strain on the heart and arteries.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Regular, heavy drinking can raise blood pressure.
- Chronic Conditions: Kidney disease, diabetes, and sleep apnea increase the risk of hypertension.

Managing Blood Pressure
Effective management of hypertension includes both lifestyle changes and medication.
- Healthy Diet: Adopt a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Weight Loss: Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly lower blood pressure.
- Limiting Alcohol: Drink alcohol in moderation.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking cessation reduces the risk of hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases.
- Reduce Salt Intake: Limit salt intake to less than 2,300 mg per day (ideally less than 1,500 mg per day).

Medications for Hypertension
- Diuretics: Help the kidneys remove sodium and water from the body.
- Beta-blockers: Reduce the workload on the heart and open blood vessels.
- ACE Inhibitors: Help relax blood vessels by blocking the formation of a natural chemical that narrows blood vessels.
- Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs): Help relax blood vessels by blocking the action of a natural chemical that narrows blood vessels.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Help relax the muscles of blood vessels.
- Alpha-blockers: Reduce nerve impulses that tighten blood vessels.
Home Remedies for Hypertension
- Garlic: Consuming raw garlic can help lower blood pressure.
- Hibiscus Tea: Drinking hibiscus tea can help reduce blood pressure.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil supplements, these can help lower blood pressure.
- Dark Chocolate: Consuming dark chocolate in moderation may reduce blood pressure.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and lower blood pressure.

Yoga for Hypertension
- Shavasana (Corpse Pose): Promotes relaxation and stress relief.
- Sukhasana (Easy Pose): Helps calm the mind and body.
- Balasana (Child's Pose): Reduces stress and relaxes the body.
- Setu Bandhasana (Bridge Pose): Opens the chest and relieves tension.
- Adho Mukha Svanasana (Downward-Facing Dog Pose): Stretches the body and improves circulation.

Monitoring Blood Pressure at Home
Regular monitoring of blood pressure at home is essential for effective hypertension management. Tips for accurate measurement include:
- Use a Validated Blood Pressure Monitor: Ensure the device is accurate.
- Measure at the Same Time Daily: Consistency is key for tracking blood pressure.
- Avoid Caffeine, Exercise, and Smoking Before Measurement: These factors can temporarily raise blood pressure.
- Rest for 5 Minutes Before Measurement: Sit quietly before taking a reading.
- Take Multiple Readings: Average the results for better accuracy.

Complications of Untreated Hypertension
If left untreated, hypertension can lead to serious complications, including:
- Heart Attack or Stroke: Hypertension can cause arteries to harden and thicken, leading to heart attack or stroke.
- Aneurysm: Increased blood pressure can cause blood vessels to weaken and bulge, forming an aneurysm.
- Heart Failure: The heart has to work harder to pump blood, leading to thickening of the heart muscles.
- Kidney Damage: Hypertension can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, affecting their ability to filter waste from the blood.
- Vision Loss: High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision loss.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Involves a combination of high blood sugar, increased waist circumference, high cholesterol levels, and high blood pressure.

Advances in Hypertension Research and Treatment
Recent advancements in hypertension research have led to new treatment options and improved management strategies. These include:
- Renal Denervation: A minimally invasive procedure that reduces nerve activity in the kidneys, lowering blood pressure.
- Implantable Devices: Devices that monitor and regulate blood pressure.
- Genetic Research: Identifying genes associated with hypertension to develop personalized treatments.
- New Medications: Development of new drugs that target specific pathways involved in blood pressure regulation.

Conclusion
Hypertension is a manageable condition with the right knowledge and tools. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies, individuals with hypertension can lead healthy, fulfilling lives. It's important to stay informed about the latest research and treatment options and to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.

Dr. Jane Doe
7 Sep 2024 • 8 min read