Heart Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Care
Dr. Jane Doe
7 Sep 2024 • 8 min read
Introduction to Heart Disease
Heart disease, also known as cardiovascular disease, encompasses a range of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. It is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Learning about the types, causes, symptoms, and treatments of heart disease is crucial for prevention and management.
What is Heart Disease?
Heart disease refers to a variety of heart conditions, including coronary artery disease, heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias), congenital heart defects, heart valve disease, and cardiomyopathy. These conditions can lead to heart attacks, chest pain (angina), or stroke.
Types of Heart Disease
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): The most common type, caused by the buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats caused by problems with the heart's electrical system.
- Heart Failure: A condition where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
- Heart Valve Disease: Problems with the valves that control blood flow through the heart.
- Cardiomyopathy: Diseases of the heart muscle that make it harder for the heart to pump blood.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Heart problems present at birth.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Narrowing of the arteries to the limbs, often associated with atherosclerosis.
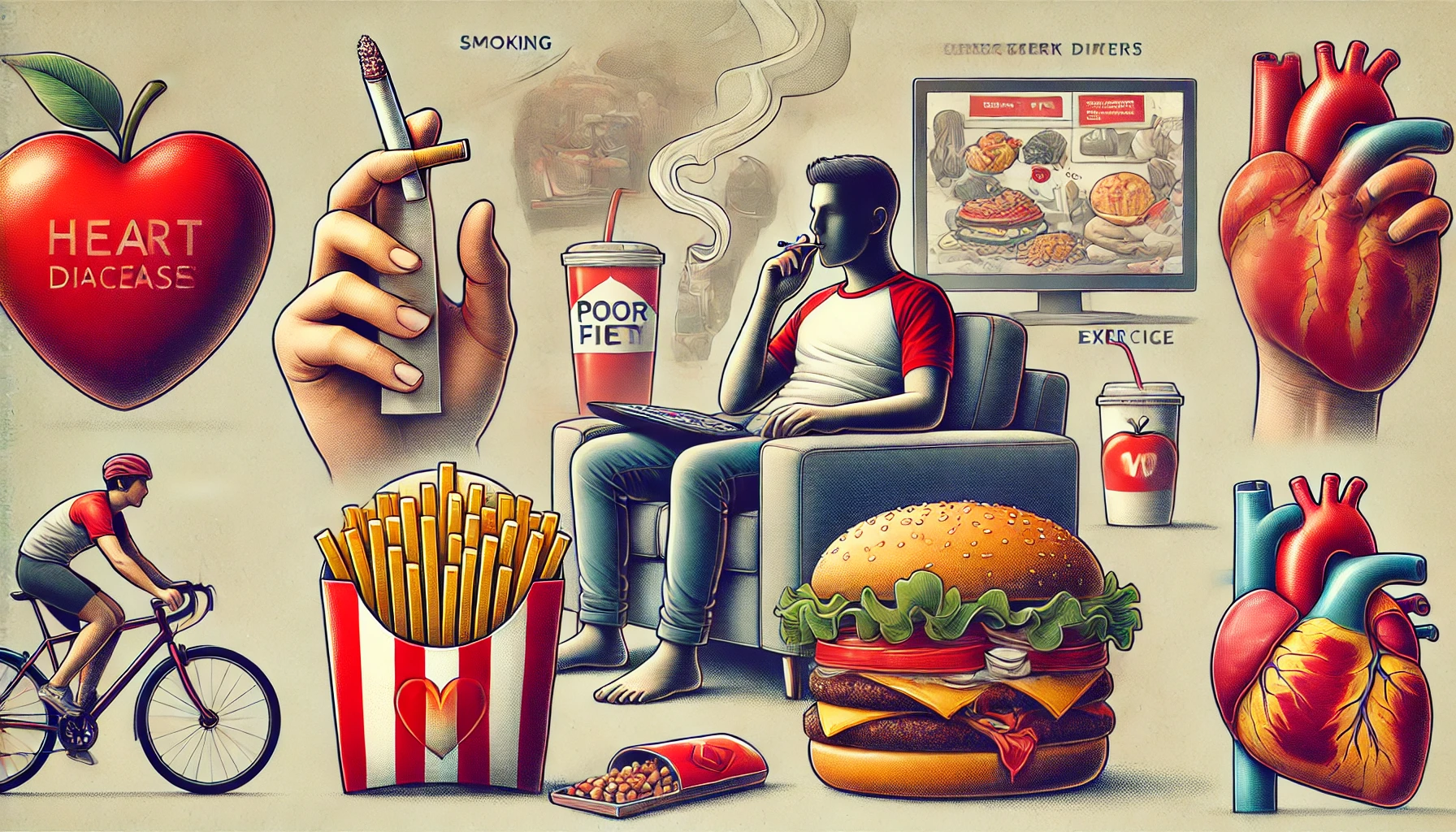
Causes and Risk Factors
Heart disease is caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. Common causes and risk factors include:
- Atherosclerosis: Buildup of plaque in the arteries.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Increases the workload of the heart.
- High Cholesterol: Leads to plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels.
- Smoking: Damages the blood vessels and the heart.
- Obesity: Increases the risk of heart disease.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity.

Symptoms of Heart Disease
- Chest Pain or Discomfort (Angina): A common symptom of heart disease.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing during physical activities.
- Pain in the Neck, Jaw, or Back: Can be a sign of heart disease.
- Irregular Heartbeats: Fluttering or a racing heart.
- Swelling in the Legs, Ankles, or Feet: A sign of heart failure.
- Dizziness or Fainting: A potential sign of arrhythmia or other heart issues.

Diagnosing Heart Disease
- Physical Examination and Medical History: The doctor will review symptoms, medical history, and risk factors.
- Blood Tests: Check for cholesterol levels, blood sugar, and other indicators.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Measures the electrical activity of the heart.
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart.
- Stress Test: Measures how the heart works during physical activity.
- Cardiac Catheterization: Involves inserting a catheter into the heart to examine the coronary arteries.
- CT or MRI: Imaging tests that provide detailed pictures of the heart and blood vessels.
Treatment Options
- Lifestyle Changes: Healthy diet, regular exercise, weight loss, smoking cessation, stress management.
- Medications: Statins to lower cholesterol, beta-blockers to reduce blood pressure and heart rate, anticoagulants to prevent blood clots, and diuretics to reduce fluid buildup.
- Surgical Procedures: Angioplasty, stent placement, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), valve repair or replacement, pacemaker, or ICD implantation.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
- Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Quit Smoking: Seek support to quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and yoga.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Drink alcohol in moderation.

Complications of Heart Disease
- Heart Attack: Occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked.
- Stroke: Occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted.
- Heart Failure: When the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats that can be life-threatening.
- Peripheral Artery Disease: Narrowing of the arteries to the limbs, leading to pain and mobility issues.
- Sudden Cardiac Arrest: An unexpected loss of heart function, breathing, and consciousness.
Advances in Heart Disease Research and Treatment
- Innovative Medications: Development of drugs that target specific pathways involved in heart disease.
- Minimally Invasive Surgeries: Techniques that reduce recovery time and improve outcomes.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Research into using stem cells to repair damaged heart tissue.
- Artificial Hearts: Development of mechanical devices to replace the function of the heart.
- Telemedicine: Remote monitoring and management of heart disease through digital health technologies.

Conclusion
Heart disease is a serious condition that requires a comprehensive approach to understanding, diagnosing, and treating. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can better manage their heart health and seek the most effective treatments available. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and support.

Dr. Jane Doe
7 Sep 2024 • 8 min read